How much hail can damage a PV system?
 namkoo solar
namkoo solar
A recent hail storm in northern Italy damaged several PV systems.
The magazine PV Italia has obtained from the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam a 2019 report that analyzes the impact of a severe hailstorm that occurred in the Netherlands in 2016, revealing the destructive nature of hailstones on solar installations. According to their assessment, damage to photovoltaic (PV) modules came mainly from hailstones with a diameter of more than 3 centimeters.
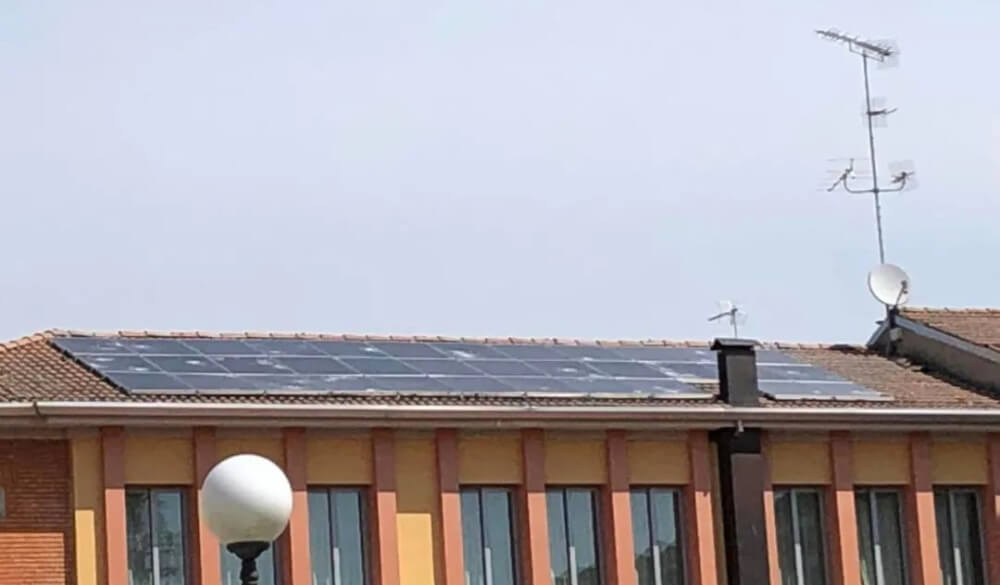

Photovoltaic systems damaged in the hail storm that hit northern Italy on July 23rd. Photo credit: Leonardo Setti
The recent hail storms that occurred in northern Italy have drawn attention to the damage that these violent and sudden atmospheric events can cause to PV systems. Some system owners have posted photos of damaged facilities on social networks, clearly showing the ferocity of the hail storms and, most importantly, the size of the hailstones, some of which were as large as 20 centimeters in diameter.
So how large a hail particle can cause damage to a PV system? How large a hailstone diameter can be considered a critical threshold above which damage becomes significant?
The Italian PV magazine attempts to answer these questions by citing a 2019 report by the Free University of Amsterdam (VUA), which investigated insured loss data from a historic hailstorm that occurred in June 2016 in the Netherlands.
According to the Dutch researchers' conclusions, damage to solar panels is mainly generated by hailstones with a diameter of more than 3 centimeters. In their article, "Vulnerability of Solar Panels to Hail," they explain, "Larger hailstones (4 centimeters or more) cause on average more damage than smaller hailstones, and they reflect a large difference in the degree of damage to solar panels."
Both hidden and visible damage can occur when hail reaches 3 centimeters in diameter, and once it reaches 4 centimeters, the percentage of visible damage occurring increases significantly.
The smallest cracks (microcracks) do not occur in the front glass layer, but rather in the silicon layer, so the damage does not initially affect the panel's power generation efficiency. However, after a few months, a rapid decrease in power may occur in the damaged area, and after about a year, microcracks may also appear on the outside of the panel. All of the damage reduces the lifespan of the solar panels.
The researchers explain that the orientation of the roof relative to the hailstorm can greatly influence the damage caused by the hailstorm to the solar panels, which may be more decisive than the size of the hailstorm's diameter in terms of the extent of damage to the panels.
On the other hand, some experience also suggests that even the angle at which solar panels are mounted can affect the extent of their damage in a hailstorm. According to the scientists' conclusions, a greater tilt will help mitigate the damage.
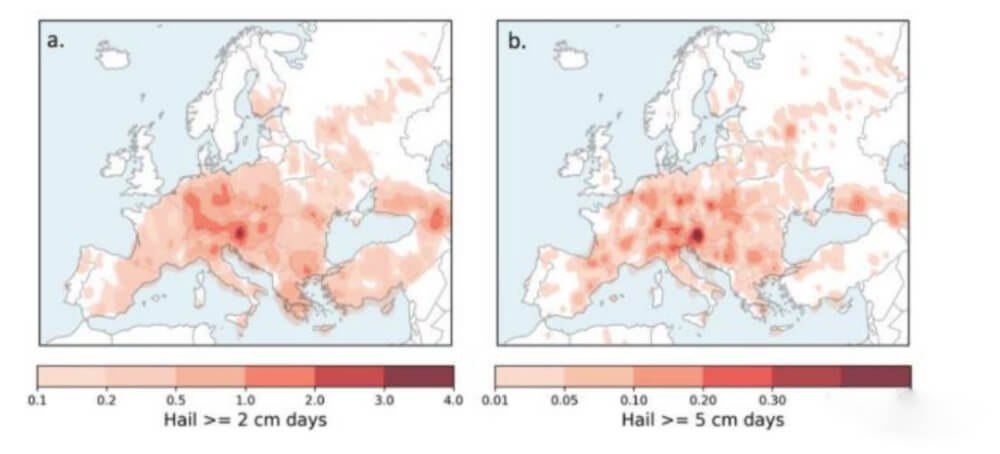
(Annual average number of days for (a) large hail and (b) very large hail (Pucik et al., 2019)
The study also shows that the frequency of hailstorms in Europe and the Netherlands is increasing, as is the damage caused by them. This suggests that exposed items, such as solar panels, may become more vulnerable in the future.
The Dutch researchers concluded, "Hail risk and the vulnerability of solar panels to hail should be integrated into risk models and climate adaptation strategies."



































